SHALE GAS AND SHALE OIL RESOURCES: PROSPECT AND CHALLENGES
• Shale gas definition
• geological conditions of occurrence
• world reserves recoverable
• India reserves locations(distribution)
• Benefits to India by harnessing shale gas
• Policy and steps taken by India in recent times
• challenges and limitations
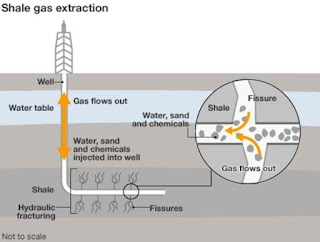
shale gas is unconventional energy resource of natural gas that is trapped within sedimentary rock formation such as shales,sandstones ,limestones. Shale has low matrix permeability, they are rich in organic material(0.5% to 25%), these petroleum source rocks under high heat and pressure has converted petroleum to natural gas by thermogenic process. Gas produced here is held in natural fractures, pore spaces or organic material is absorbed. This natural gas trapped is utilled by USA in recently upto 40% efficiency.
According to EIA, the estimated world shale gas resources is 7576 trillion cubic feet (tcf) comprising of 48 countries across the world(till sept 2015). China leads the technically recoverable shale gas. USA last year slipped to 4th rank from 2nd rank.
But the shale gas is produced commercially only by USA, Canada and China. While China has ambitious plans to increase its shale gas production. There are 3 factors to make shale gas production economically viable:
1) technology advances in horizontal drilling
2) hydraulic fracturing; and
3) Increase in natural gas prices in the global market.
Due to improved horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing there is a increased recoverable potential as high as 54%. the figure below provides the projected potential development of shale gas in the year 2035 in major countries:
Shale gas resource in India
• Shale gas definition
• geological conditions of occurrence
• world reserves recoverable
• India reserves locations(distribution)
• Benefits to India by harnessing shale gas
• Policy and steps taken by India in recent times
• challenges and limitations
shale gas is unconventional energy resource of natural gas that is trapped within sedimentary rock formation such as shales,sandstones ,limestones. Shale has low matrix permeability, they are rich in organic material(0.5% to 25%), these petroleum source rocks under high heat and pressure has converted petroleum to natural gas by thermogenic process. Gas produced here is held in natural fractures, pore spaces or organic material is absorbed. This natural gas trapped is utilled by USA in recently upto 40% efficiency.
According to EIA, the estimated world shale gas resources is 7576 trillion cubic feet (tcf) comprising of 48 countries across the world(till sept 2015). China leads the technically recoverable shale gas. USA last year slipped to 4th rank from 2nd rank.
But the shale gas is produced commercially only by USA, Canada and China. While China has ambitious plans to increase its shale gas production. There are 3 factors to make shale gas production economically viable:
1) technology advances in horizontal drilling
2) hydraulic fracturing; and
3) Increase in natural gas prices in the global market.
Due to improved horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing there is a increased recoverable potential as high as 54%. the figure below provides the projected potential development of shale gas in the year 2035 in major countries:
Shale gas exploration is a challenge due to:
1) completely onland
2) leaves greater footprints
3) tightness of shale gas reservoirs
4) hydraulic fracking involves large land areas, multistage fracturing and frequent simulation.
5) The various phases of the shale gas development,life cycle and their associated issues as follows:
Drill pad construction and operation
Hydraulic fracturing and flowback water management
Groundwater contamination
Blowouts and house explosions
Water consumption and supply
Spill management and surface water protection
atmospheric emissions
health effects
6) water requirements is from few thousands to 20 thousand cubic meters per well in fracking technology. usages of chemicals mixed water contaminates water resources.
7) Local water issues of availability and water disposal and threat to environment.
8) Vast land cover required compared to conventional oil and gas, put pressure on land. For example from an hydrocarbon drill area of 10 sq.km requires 25000 sq.km.
9) Proppants injections per well 1000-4000 tonnes per well feared earthquake risks
So, every country which embarks on shale gas exploitations regime must plan
adequate regulatory regime
adequate environmental standards to safeguard against any long term damages to environment
water being a scarce resource in India, particularly calls for strengthening of local institutions in undertaking baseline studies, monitoring of water quality and water balance.
Shale gas resource in India
India holds shale gas in all 26 sedimentary basins not only 7 hydrocarbon producing basins. according to EIA technically recoverable shale gas is about 96 tcf from these sedimentary basins:-
1) cambay
2) Krishna-godavari
3) Cauvery
4) Damodar valley
5) Upper Assam
6) Pranhita-godavari
Shale gas exploration in India leads to several benefits:-
• Helps to meet the growing demand of natural gas for energy needs.
• To reduce its dependence on expensive energy imports and the energy import bill.
• The development in this sector can boost economic activities,increase government revenues and creates new jobs.
• attract investment in gas pipeline infrastructures and associated downstream segments to cater the latent gas demand in the country.
• application of gas in new sector such as industrial and commercial establishments in the ceramics,chemicals,glass,textiles,pharmaceuticals,and diamond industries.
• It could be a viable alternative for meeting the need of peak and captive power units and other sectors such as transportation, refineries and steel where it can substitute expansive liquid fuels.
Requirements or prerequisites for shale gas industry development in India are:-
• Supportive regulatory framework means fiscal incentives to reduce the cost of exploration and operations. since ,the its cost is higher than oil and gas in india like USA and China.
• To encourage development of service capabilities since our geological terrains are different ,imported equipments and technology need to be modified, indigenous research and development services to developed.
• To address environmental concerns associated with hydraulic fracturing such as health, water contamination,etc, environmental impact assessment studies, monitoring and reporting.
• Address social concerns related to vast land requirement leads to displacement, physical footprint , etc.
• overcome talent shortfall—human resource development.
Latest developments in shale gas field in India:-
• in 2012 , the directorate general of hydrocarbon(DGH) submitted its draft policy on exploitation of shale gas to the ministry of petroleum and natural gas (MoPNG).
• In 2013, the government has set up a multi-organizational team comprising of the DGH, ONGC, OIL, and GAIL to analyze existing data set and suggesting a methodology for shale gas development in the country.
• ONGC and OIL are aggressively implementing pilot projects to assess the shale gas potential in the country. In addition. GAIL and RIL entered into USA to gain technical expertise to apply in India.
• In 2018, India allows companies to explore and exploit the unconventional hydrocarbons under their old contracts. So, state-run companies can unlock the country's potential for shale oil and gas.
• The oil ministry had amended the Petroleum and Natural Gas Rules 1959 to include shale in the definition of petroleum. India currently has around 100-200 TCF of shale gas reserves from 5 sedimentary basins.
• Helps to meet the growing demand of natural gas for energy needs.
• To reduce its dependence on expensive energy imports and the energy import bill.
• The development in this sector can boost economic activities,increase government revenues and creates new jobs.
• attract investment in gas pipeline infrastructures and associated downstream segments to cater the latent gas demand in the country.
• application of gas in new sector such as industrial and commercial establishments in the ceramics,chemicals,glass,textiles,pharmaceuticals,and diamond industries.
• It could be a viable alternative for meeting the need of peak and captive power units and other sectors such as transportation, refineries and steel where it can substitute expansive liquid fuels.
Requirements or prerequisites for shale gas industry development in India are:-
• Supportive regulatory framework means fiscal incentives to reduce the cost of exploration and operations. since ,the its cost is higher than oil and gas in india like USA and China.
• To encourage development of service capabilities since our geological terrains are different ,imported equipments and technology need to be modified, indigenous research and development services to developed.
• To address environmental concerns associated with hydraulic fracturing such as health, water contamination,etc, environmental impact assessment studies, monitoring and reporting.
• Address social concerns related to vast land requirement leads to displacement, physical footprint , etc.
• overcome talent shortfall—human resource development.
Latest developments in shale gas field in India:-
• in 2012 , the directorate general of hydrocarbon(DGH) submitted its draft policy on exploitation of shale gas to the ministry of petroleum and natural gas (MoPNG).
• In 2013, the government has set up a multi-organizational team comprising of the DGH, ONGC, OIL, and GAIL to analyze existing data set and suggesting a methodology for shale gas development in the country.
• ONGC and OIL are aggressively implementing pilot projects to assess the shale gas potential in the country. In addition. GAIL and RIL entered into USA to gain technical expertise to apply in India.
• In 2018, India allows companies to explore and exploit the unconventional hydrocarbons under their old contracts. So, state-run companies can unlock the country's potential for shale oil and gas.
• The oil ministry had amended the Petroleum and Natural Gas Rules 1959 to include shale in the definition of petroleum. India currently has around 100-200 TCF of shale gas reserves from 5 sedimentary basins.